In the current global context of energy crisis, hydrogen energy has garnered widespread attention as a secondary energy source that is abundant, green, low-carbon, and widely applicable. Accompanying the practical applications of hydrogen energy in power generation, industry, and transportation, numerous countries worldwide have successively released strategic roadmaps for hydrogen energy development, primarily focusing on promoting the hydrogen energy and fuel cell industries in the power generation and transportation sectors.
China has similarly focused its attention on hydrogen energy development. In March 2019, hydrogen energy was first incorporated into China’s “Government Work Report,” accelerating the construction of charging and hydrogen refueling facilities in the public domain. In April 2020, the “Energy Law of the People’s Republic of China (Draft for Comments)” proposed to include hydrogen energy within the energy category. In October 2021, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council issued the “Opinions on Completely, Accurately and Comprehensively Implementing the New Development Concept to Achieve Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality,” coordinating the development of the entire hydrogen energy chain from “production-storage-transportation-utilization.” In March 2022, the National Development and Reform Commission released the “Medium and Long-term Plan for Hydrogen Energy Industry Development (2021-2035),” designating hydrogen energy as an important component of the future national energy system and a crucial carrier for the green and low-carbon transformation of end-use energy consumption. The hydrogen energy industry was identified as a strategic emerging industry and a key development direction for future industries. In February 2024, the “Green and Low-Carbon Transformation Industry Guidance Catalogue (2024 Edition)” incorporated the entire chain of hydrogen energy “production-storage-transportation-utilization” equipment manufacturing as a key emerging green and low-carbon transformation industry, guiding policies and resources to support the healthy development of related industries.
In recent years, China’s hydrogen energy industry has developed rapidly, essentially encompassing the entire chain of hydrogen production, storage, transportation, and utilization. The country has preliminarily mastered the main technologies and production processes for hydrogen production, storage and transportation, refueling, fuel cells, and system integration. Currently, China is the world’s largest hydrogen producer. The majority of its hydrogen production, approximately 80%, is derived from coal gasification, with a total hydrogen production capacity of about 33 million tons. Three major regional hydrogen energy industrial clusters are gradually taking shape in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the Yangtze River Delta, and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. A multi-stakeholder, integrated innovation-driven hydrogen energy industrial ecosystem is progressively forming. Significant breakthroughs have been achieved in two key technologies: water electrolysis for hydrogen production and hydrogen fuel cells.
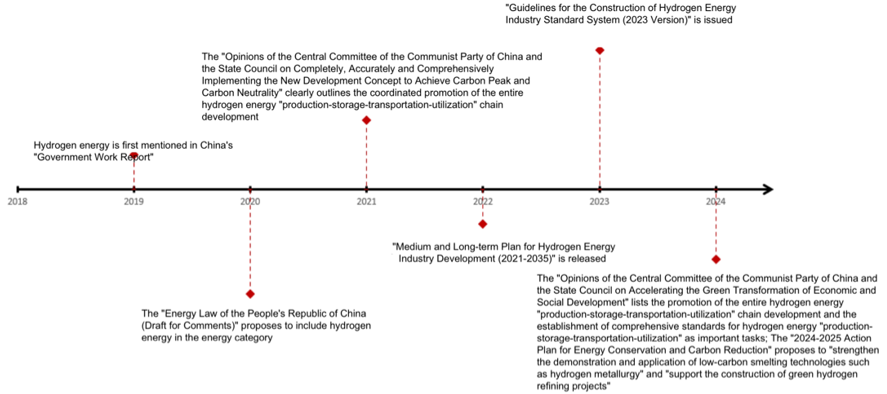
Figure 1: Timeline of Hydrogen Energy Development Policies Introduced in China
1. Main Directions and Objectives of China’s Medium and Long-term Hydrogen Energy Development
Hydrogen energy development plays a crucial role in achieving the “dual carbon” goals. In October 2021, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council issued the “Opinions on Completely, Accurately and Comprehensively Implementing the New Development Concept to Achieve Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality,” which proposed important tasks related to hydrogen energy development, including “coordinating the development of the entire hydrogen energy chain from ‘production-storage-transportation-utilization’,” “promoting the construction of hydrogen refueling stations,” “advancing research on low-carbon frontier technologies such as renewable energy hydrogen production,” and “strengthening research and development, demonstration, and large-scale application of key technologies for hydrogen energy production, storage, and application.”
In line with the “dual carbon” goals, in March 2022, the National Development and Reform Commission and the National Energy Administration publicly released the “Medium and Long-term Plan for Hydrogen Energy Industry Development (2021-2035)” as one of the “N” components in the “1+N” policy system for carbon peak and carbon neutrality. The Plan clearly defines China’s hydrogen energy industry development goals for 2025, 2030, and 2035.
By 2025, a relatively complete institutional policy environment for hydrogen energy industry development will be formed. Industrial innovation capabilities will be significantly improved, with core technologies and manufacturing processes basically mastered, and a relatively complete supply chain and industrial system initially established. Hydrogen energy demonstration applications will achieve notable results, with significant progress in clean energy hydrogen production and hydrogen storage and transportation technologies. Market competitiveness will be substantially enhanced, and a hydrogen energy supply system primarily based on industrial by-product hydrogen and nearby utilization of renewable energy hydrogen production will be initially established. The number of fuel cell vehicles will reach approximately 50,000, with a number of hydrogen refueling stations deployed and constructed. Renewable energy hydrogen production will reach 100,000-200,000 tons/year, becoming an important component of new hydrogen energy consumption, and achieving carbon dioxide emission reductions of 1-2 million tons/year.
By 2030, a relatively complete hydrogen energy industry technology innovation system and clean energy hydrogen production and supply system will be formed. The industrial layout will be rational and orderly, with widespread application of renewable energy hydrogen production, strongly supporting the realization of the carbon peak goal.
By 2035, a hydrogen energy industrial system will be formed, constructing a diverse hydrogen energy application ecosystem covering transportation, energy storage, industrial, and other fields. The proportion of renewable energy hydrogen production in terminal energy consumption will significantly increase, playing an important supporting role in the green transformation and development of energy.
2. Trends in China’s Hydrogen Energy Development Policy Formulation
The “Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Accelerating the Green Transformation of Economic and Social Development” promotes the development of the entire hydrogen energy “production-storage-transportation-utilization” chain. It aims to improve the infrastructure network of charging (swapping) stations, hydrogen (methanol) stations, and shore power, and accelerate the construction of urban smart transportation management systems. The document also emphasizes the improvement of urban and rural logistics distribution systems, promoting green and intelligent transformation of distribution methods, and establishes the development of standards for hydrogen “production-storage-transportation-utilization” as important tasks.
2.1 Top-down, Locally Adapted Layout for a New Pattern of Hydrogen Energy Development
The “Medium and Long-term Plan for Hydrogen Energy Industry Development (2021-2035)” analyzes the current development status of China’s hydrogen energy industry, clarifies the strategic positioning, overall requirements, and development goals of hydrogen energy in China’s green and low-carbon energy transition, and proposes specific plans for hydrogen innovation systems, infrastructure, diverse applications, policy support, and organizational implementation.
Based on coordinating the national hydrogen energy industry layout, the Plan proposes specific requirements for hydrogen infrastructure construction and safety management, aiming to accelerate the construction of a safe, stable, and efficient hydrogen supply network. It also requires local regions to choose hydrogen production technology routes according to their resource endowments and industrial layout, gradually promoting the construction of a clean, low-carbon, and low-cost multi-element hydrogen production system. Regarding the construction of storage and transportation systems and hydrogen refueling stations, the Plan emphasizes the demand-oriented principle, promoting the orderly construction of hydrogen energy industry facilities based on diversification and appropriate scale.
The “Outline of the 14th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and Long-Range Objectives Through the Year 2035” lists “hydrogen energy and energy storage” as future industries requiring organized implementation of incubation and acceleration plans. Subsequently, various provinces and cities in China have incorporated hydrogen energy industry development into their “14th Five-Year Plan.” Following the issuance of the “Medium and Long-term Plan for Hydrogen Energy Industry Development (2021-2035),” local regions have successively issued in-depth planning policy documents for hydrogen energy industry development tailored to local conditions.
In August 2022, ten departments including the Shanghai Municipal Development and Reform Commission, Shanghai Municipal Economic and Information Technology Commission, and Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission jointly released the “Several Policies on Supporting High-Quality Development of Hydrogen Energy Industry in China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone Lingang New Area.” In November of the same year, based on the good results achieved in the implementation of the solar-powered water electrolysis hydrogen production and comprehensive application demonstration project outlined in the “Guiding Opinions on Accelerating the Cultivation of Hydrogen Energy Industry Development,” the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Development and Reform Commission issued the “Hydrogen Energy Industry Development Plan for Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region.” In August 2023, the Xinjiang Autonomous Region Development and Reform Commission issued “Several Policy Measures to Support the Construction of Hydrogen Energy Industry Demonstration Zones in the Autonomous Region.”
2.2 Standardized Guidance, Building a Comprehensive Hydrogen Energy Industry Chain Standard System
In July 2023, six departments including the State Administration for Market Regulation, the National Development and Reform Commission, and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology jointly issued the “Guidelines for the Construction of Hydrogen Energy Industry Standard System (2023 Version),” providing guidance and regulations for establishing a standard system for hydrogen production, storage, transportation, and utilization. In March 2024, eighteen departments, including the State Administration for Market Regulation, the Cyberspace Administration of China, and the National Development and Reform Commission, jointly issued the “Action Plan for Implementing the National Standardization Development Outline (2024-2025),” which again emphasized the need to “accelerate the supply of standards for the entire hydrogen energy industry chain and improve the standard system for new energy storage.”
The Guidelines focus on the coordination of upstream and downstream standards in the industry chain, primarily addressing low-carbon hydrogen production, efficient hydrogen storage and transportation, reliable hydrogen refueling, and diversified hydrogen energy applications. It systematically constructs a framework for hydrogen energy industry standards, covering 111 existing national and industry standards, 28 national and industry standards under development, and 19 planned national and industry standards.
The Guidelines focus on the coordination of innovative technologies and standards, paying particular attention to key core technologies and products in various stages of hydrogen production, storage, transportation, and utilization. It aims to synergistically promote technological innovation, standard development, and industrial growth, using standards to facilitate the transformation of technological innovation achievements. The Guidelines fully mobilize the enthusiasm of industry, academia, research institutions, and end-users to accelerate the development of standards in areas such as hydrogen safety, hydrogen transportation pipelines, hydrogen refueling station equipment, fuel cell systems and their components, and fuel cell vehicles.
The Guidelines emphasize the coordination of domestic and international standards. While developing domestic standards, they actively promote the improvement of international standardization levels for hydrogen energy. The Guidelines aim to enhance the international standardization capabilities of enterprises, research institutions, and universities, encouraging participation in international hydrogen energy standardization work, and transforming China’s advanced technologies and application experiences in the hydrogen energy field into international standards.
2.3 Future Outlook: Developing Multi-Industry Applications of Hydrogen Energy
In February 2024, seven departments, including the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the National Development and Reform Commission, and the Ministry of Finance, issued the “Guiding Opinions on Accelerating the Green Development of Manufacturing Industry.” This document pointed out the need to “construct a technology and equipment system for the entire hydrogen energy industry chain, including production, storage, transportation, and utilization, focusing on hydrogen demand in petrochemicals, steel, transportation, energy storage, and power generation sectors, to improve the economic viability of hydrogen energy technology and the completeness of the industry chain.” In March, the “Action Plan for Promoting Large-scale Equipment Renewal and Trade-in of Consumer Goods” clearly stated the need to strengthen the industrialization capacity of green aviation equipment such as electric and hydrogen-powered aircraft. In May, the State Council issued the “2024-2025 Action Plan for Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction,” proposing to “strengthen the demonstration and application of low-carbon smelting technologies such as hydrogen metallurgy, encourage the research and development of renewable energy hydrogen production technologies, support the construction of green hydrogen refining projects, and gradually reduce the industry’s coal-based hydrogen consumption.” In August, six pilot tasks for promoting and applying new energy and clean energy vehicles and equipment, including creating demonstration application scenarios for the hydrogen energy logistics industry chain, were selected as part of the first batch of special pilot tasks for building a green and low-carbon transportation power.
In March 2024, the General Office of the National Development and Reform Commission issued the “List of Green and Low-Carbon Advanced Technology Demonstration Projects (First Batch).” The list includes five green hydrogen carbon reduction pilot demonstration projects to be implemented in Hebei, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Jiangsu, and other regions.
Table 1: List of Green and Low-Carbon Advanced Technology Demonstration Projects (Green Hydrogen Carbon Reduction Projects)
| No. | Project name | Region | Implementing entity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zhangjiakou Wind-Hydrogen Integrated Source Network Load Storage Comprehensive Demonstration Project (Phase I) | Hebei | Hebei Guochuang Hydrogen Energy Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 2 | Demonstration Project for “Electricity-Hydrogen-Electricity” New Mode Based on Pure Hydrogen Fuel Cell Innovation | Neimenggu | State Power Investment Corporation Beijing Heavy Fuel Energy Technology Development Co., Ltd., Neimenggu Huaneng Dalate Aluminum Power Co., Ltd. |
| 3 | 500,000 kW Wind Power Hydrogen Production and Ammonia Production Integration Demonstration Project | Neimenggu | China Shipbuilding Group Wind Power Development Co., Ltd. |
| 4 | Hydrogen Energy Industrial Park (Green Hydrogen-Ammonia Integration) Demonstration Project | Jilin | Energy Construction Green Hydrogen New Energy (Songyuan) Co., Ltd. |
| 5 | High-Parameter Liquid Hydrogen Storage and Transportation Equipment Project | Jiangsu | Aerospace Chenguang Co., Ltd. |
3. Current Issues and Future Development Trends in China’s Hydrogen Energy Industry
Despite China’s strong foundation in hydrogen production and a large-scale application market, it is still in the early stages of development and faces numerous challenges. In terms of transportation, China primarily relies on road transportation methods such as long-tube trailers for hydrogen transport. Compared to foreign countries, China’s hydrogen storage density is low, and the degree of lightweight design is insufficient. Moreover, some key technologies are not yet fully autonomous and controllable. In the future, China will promote the industrial application of cryogenic liquid hydrogen storage and transportation, and carry out demonstration pilots for hydrogen-blended natural gas pipelines and pure hydrogen pipelines to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Regarding costs, China’s hydrogen production, storage, and transportation costs are relatively high, limited by the low level of technological equipment and unresolved technical barriers in key materials and core technologies. In the future, costs will be reduced through technological advancements, scaled production, supplemented by policy support and improved market mechanisms. In terms of hydrogen storage, current high-pressure gaseous hydrogen storage poses significant safety risks and low storage density, while China’s liquid and solid hydrogen storage technologies are still in the research and development stage with high costs. It is expected that China will improve hydrogen storage efficiency and reduce costs by increasing storage pressure and developing liquid and solid hydrogen storage technologies.
Furthermore, China is orderly promoting the vigorous development of the hydrogen energy industry through the “Medium and Long-term Plan for Hydrogen Energy Industry Development (2021-2035),” including establishing and improving hydrogen energy safety supervision systems and standards, strengthening the prevention and control of major safety risks across the entire industry chain, and enhancing the level of comprehensive safety management.
 China, Policy Developments Related to Hydrogen Energy
China, Policy Developments Related to Hydrogen Energy
























