1. Current status of occupational health and safety management in China
In China, in order to ensure the safety and health of workers, the safety management of production is being strengthened by the “Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development” and “Safe Production Law”. In particular, the “Safety Production Law” that came into effect in 2002 has been seriously considered for the improvement since its enforcement, and, as a result, Western standards have been adopted as national standards or industry standards in China; for instance, companies are required to establish strict safety production conditions for their employees. When a non-conformity is found through on-site inspection by the supervisory authority, a correction order is issued, and if improvement cannot be made, the production license is revoked at worst. Authorities are also actively promoting safety production standardization grade assessments. Companies that cannot obtain Level 3 certification in this grade evaluation may be subject to revocation of production licenses. It may also pose a great risk to Japanese companies that have already been involved in production in China. Therefore, it is necessary for such producers to tackle on this grade evaluation issue with sufficient preparation.
However, indeed in China, there are few companies that have obtained corporate safe production standardization certification; therefore, there are remaining many problems associated with safe production. According to the “Progress Report on Measures Intensified for Safe Production with Focus on Hazardous Chemicals” released by the Emergency Management Department in December 2019, individual regions are taking measures for safe production according to the characteristics of each region, but various problems still remain. Some examples are as follows;
Efforts in Local Provinces
From January to November 2019, a total of 23,436 companies handling hazardous chemicals were inspected by the Emergency Management Department of Sichuan province; as a result, 26,419 safety related problems were detected, and many companies were punished with various penalties. Specifically, 56 companies received suspension of operation or correction recommendations, 3 companies received temporary revocation of operating permits, 8 companies were closed, and 158 companies were also accused to be liable. The total fine amounted to 9.81 million yuan.
In addition to Sichuan province, Hubei, Anhui, Liaoning, Guangdong, Shanxi and other provinces are also taking their own individual measures.
On the other hand, according to the “2018 China Hygiene and Health Project Development Statistics Bulletin” released by the National Health and Welfare Committee, 23,497 occupational diseases occurred as a total throughout China in 2014, of which 19,524 were occupational pneumoconiosis and there were 1,333 cases of chemical poisoning and 540 cases of occupational infectious diseases. Then, poisoning suffocation accidents, gas explosion accidents, and hydrogen sulfide gas poisoning accidents occurred frequently.
2. New safe production permit
The new safe production permit was applied from March 1, 2020. The old version of the safe production license applied so far can still be used, but it is also possible to apply for switching to the new version of the safe production permit.
The precautions regarding the use of the new safe production permit are as follows;
- The new edition safety production permit has an officially certified copy and a duplicate copy. The size of the official copy is 297 mm (height) x 420 mm (width), and the size of the duplicate copy is 210 mm (height) x 297 mm (width). Both the official and duplicate copies will be printed based on the relevant requirements of the “Printing Standards for New Safety Production Permit”.
- A two-dimensional code will be added to the new safe production permit, and scanning will enable cooperation among the “electronic certification systems” in each region. The two-dimensional code is generated according to the “new safety production permit two-dimensional code explanation”.
- The Emergency Management Department outsources the production of printing films, samples of watermark paper, and print templates for new safety production permits, to specialized factories, and provides them free of charge to the emergency management agencies (bureaus) at each province level, with supports for related technologies.
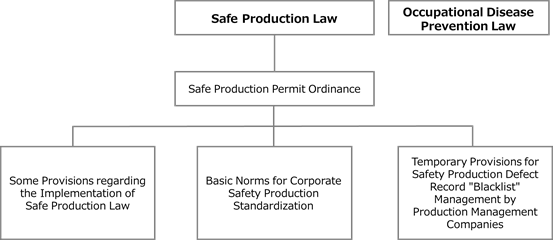
3. Legal and regulatory framework for occupational health and safety
In China, as described above, the “Safe Production Law” came into effect in 2002, then Western-style standards have been adopted as national standards or industry standards; as a result, under these laws and standards, companies are required to establish strict safety production conditions for their workers.
 Occupational safety and health in China
Occupational safety and health in China
























