Overview about energy conservation regulations in China
In the 21st century, China’s economy is rapidly developing, while the ecological environment is gradually deteriorating. Problems have become more serious due to the extensive use of resources, and the contradiction between economic development and the resource environment is becoming more and more prominent. In the “Outline of the 11th Five-Year Plan for the National Economy and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China” released in 2006, China initially set a target of reducing energy consumption per unit of GDP (RMB 10,000) by about 20%. In 2007, the previous version of China’s Energy Conservation Law, which was enacted in November 1997, was revised to establish a national policy on energy conservation: Energy conservation is a fundamental national policy of our country, and the government shall implement an energy development policy that balances “conservation” and “development” and gives priority to “conservation”.
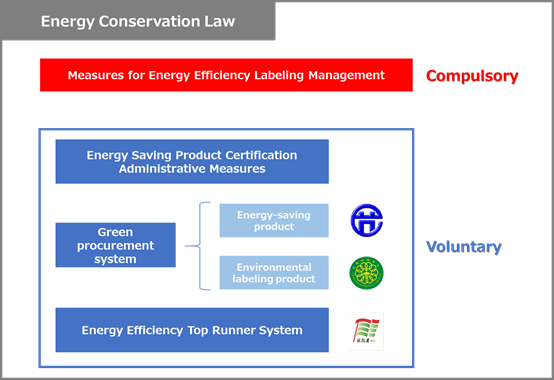
In addition, the “Energy Conservation Law of People’s Republic of China” establishes the general basic policies for energy conservation, and energy conservation policies for products, including energy efficiency labeling management, certification and government procurement for energy-saving product. In order to align with the implementation of energy efficiency labeling management, “Measures for Energy Efficiency Labeling Management” was published in August 2004 (revised in 2016). It stipulates the implement measures of energy efficiency labeling for compulsory subject products. Furthermore, more detailed regulations and standards related to the subject products and certification were formulated and released one after another.
In order to establish a complete energy conservation system, the Chinese government has established various kinds of voluntary certification systems to promote energy conservation, which were based on the “China Energy Saving Product Certification Administrative Measures”, the “Energy Efficiency Top Runner System Implementation Plan”, the government green procurement system, and the environmental protection “Top Runner” system.
Energy Conservation Law
The “Energy Conservation Law of People’s Republic of China” was enacted on November 1, 1997 (enforced on January 1, 1998). The current law was revised and promulgated on October 28, 2007 and came into effect on April 1, 2008. It establishes basic policies for energy conservation in general and energy conservation policies for all energy-consuming products. In terms of products, the law mainly makes provisions to the following three aspects.
“Energy efficiency labeling management”-Compulsory
The state has established compulsory energy efficiency standards for energy-consuming products and equipment, and energy consumption limit standards of per unit product that has a high energy consumption in the production process.
For the household appliances that are widely used and have relatively high energy consumption, such as home appliances, the state implements the energy efficiency labeling management. Producers and importers must display energy efficiency labels on the product packaging or in the instruction manual. In addition, they have to register and store them with the relevant authorities.
“Certification of energy-saving product”- Voluntary
On a voluntary basis, producers and sellers of energy-consuming products may submit an application for energy-saving product certification. After passing the certification, an energy-saving product certification certificate will be issued, and the certification mark can be used on the energy-consuming product or its packaging.
“Government Procurement”
A government purchasing list of energy-saving products and equipment was made by government, the products and equipment, which have obtained energy-saving product certification, will be given priority in the list.
Labeling system related to energy conservation
The following table is a summary of the overview of each labeling system related to energy conservation in China.
| Name | Energy efficiency labels | Energy-saving certification | Top Runner for Energy Efficiency | Green Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| property | Compulsory | Any | Any | Any |
| related law | Energy Efficiency Label Management Law | China Energy Saving Product Certification Administrative Measures | Energy Efficiency Top Runner System Implementation Plan | Opinions of the General Office of State Council on Establishing a Unified System for Green Product Standard, Certification and Labeling |
| Start year | 2005 | 1999 | 2014 | 2016 |
| Labels. |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Overview | Target products are required to be labeled (the highest level is grade 1), and the sale of target products without labeling is prohibited. The Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) is used in the inspection of determining the label grade. | A system of conducting certification by the China Standardization and Certification Center (CSC), which is a third party organization. Energy-saving product certification certificates and energy-saving labels are issued by the State Administration for Market Regulation and Certification and Accreditation Administration of P.R.C. Energy-saving product certification certificates and labels are valid for four years. Certified products are eligible for preferential purchasing under the green procurement system and preferential policies for energy-saving products. | The system is made to promote energy conservation and emission reduction in the whole society by taking measures such as selecting the top runners in the following three areas: energy-consuming products, energy-intensive industries, and public institutions, and strengthening incentive measures that contribute to improving energy consumption efficiency. | This is a system that is being promoted in order to promote the unification of standards and labels for environmentally friendly green products. The target products are the items in the “Green Product Certification List” of Certification Activity 1, and the items included in the system jointly promoted with relevant national organizations belonging to other green product conformity assessment activities (including products subject to China RoHS). |
Energy efficiency labels
| Labels. | related laws | property | Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Energy Efficiency Label Management Law | Mandatory |
|
|||
List of target products (as of May 2021)
- Household refrigerator
- Room air conditioner
- Electric washing machine
- Packaged unit type air conditioner
- Fluorescent lamp with built-in ballast for general lighting
- High-pressure sodium lamp
- Chiller (water cooler)
- Small and medium-sized three-phase asynchronous motors
- Domestic instantaneous gas water heaters
- Inverter type room air conditioner
- Multi air conditioner
- Hot water storage type electric water heater
- Household electromagnetic cooker
- Computer monitor
- Copiers, printers, facsimiles
- Automatic electric rice cooker
- AC fan
- AC contactor (contactor)
- Volumetric Compressors
- Power transformer
- Ventilator
- Flat-panel television (TV)
- Domestic microwave ovens and similar applications
- Digital broadcasting receiver
- Refrigeration showcase with separate freezer
- Solar water heating system for home use
- Microcomputer
- Exhaust fan
- Heat pump water heater
- Household gas stove
- Commercial gas stove
- Water source (geothermal) heat pump unit
- Lithium Bromide Absorption Water Chiller
- LED lamps with built-in non-directional ballast for general lighting
- Projector
- AC exhaust fans for household and similar applications
- Commercial cold storage with built-in compressor unit
- Permanent magnet synchronous motor
- Air cleaner
- LED lighting fixtures for road and tunnel lighting
- Ducted air conditioning unit
- Low ambient temperature air heat source heat pump (chilled water) unit
Implementation plan for the energy efficiency top runner system (energy efficiency “top runner” system implementation plan)
Products and industries covered by the system:
According to the plan, the system covers three sectors: energy-consuming products, energy-intensive industries, and public institutions. Currently, the following products and industries are listed as key targets for each sector, it plans to further expand the scope in the future.
- Energy-consuming products:
Home appliances such as air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, etc. - Energy-intensive industries:
Thermal power generation units, steel, petrochemicals, building materials, etc. - Public institutions:
Schools, hospitals, etc.
Products subject to the top runner system for environmental preservation
By comprehensively considering the environmental impact, market size and potential, direction of technology development and the related environmental standards, products that have a large usage volume, a large potential for reducing pollution emissions, a complete set of relevant standards, or with mature environmental friendly alternative technologies are targeted to implement the “top runner” system, which in terms of reducing the sources of pollution caused by air, water, solid waste, noise, etc. And in the future, the target will be gradually expanded to other products.
 China energy saving label
China energy saving label
























